South Australian Medical Heritage Society Inc
Website for the Virtual Museum
Home
Coming meetings
Past meetings
About the Society
Main Galleries
Medicine
Surgery
Anaesthesia
X-rays
Hospitals,other organisations
Individuals of note
Small Galleries
Ethnic medicine
- Aboriginal
- Chinese
- Mediterran
Old Physiotherapy Treatment Apparatus
Acknowledgement:
These illustrated physiotherapy treatment items are preserved in the Heritage Museum of the
Royal Adelaide Hospital, and were photographed with the kind permission and co-operation of
the curator, Rose Wilson.
The following ultraviolet lamps were formerly used by the Physiotherapy department for the treatment of Vitamin D. deficiency, and for the sterilization of open wounds, and in certain dermatological conditions.
These lamps resemble ordinary "indoor" flood lamps. They contain a high-pressure mercury arc
tube and a tungsten filament, used as a ballast, to vaporize the mercury. When first started,
the light is mainly incandescent light. When the mercury lamp warms up, the green-bluish
white colour of the mercury light is more apparent.
The lamps are usually enclosed in quartz glass transparent to U.V. radiation.
Since these lamps rely mainly on the UVB frequency for tanning, they are more likely to cause sunburn and skin cancer than UVA sun tanning lamps (which are not completely safe either). UVB lamps are also particularly irritating and harmful to eyes, so that protective goggles had to be worn by the patient.
Ultrasound therapy was first used in 1940. The ultrasonic vibrations produce heat in soft tissues, and were used in the treatment of muscular injuries and rheumatic conditions. It does not pass through bone. An electronic circuit induces ultrasonic vibrations in a crystal in the transducer held by the physiotherapist.

Short Wave Diathermy
Short Wave diathermy current is a high frequency alternating current. The heat energy obtained from the wave is used for giving relief to the patient. Its frequency is 27 MHz (now the C.B. radio-band) and the wavelength of 11 meters is in the short wave radio band. The output can be continuous or pulsed, in the machine illustrated the pulse rate can be adjusted.
With capacitor field treatment, the treatment site is placed between the plates of a capacitor and becomes the dielectric. The RF energy is diffused through the part of the body located between the plate electrodes.
In 1940, during World War 2, following the defeat of France, the Germans believed that Britain
could be forced to surrender following a sustained night bombing campaign. Attempts to secure
air superiority during daylight having failed (The Battle of Britain).
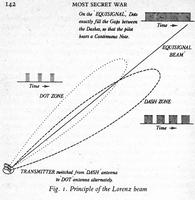
In order to guide the bombers to the target city at night they had devised a system of radio
beams, working on 30 MHz (see diagram).
The existence of the suspected beams was confirmed by an RAF aeroplane, the frequency was known from the examination of the receiver in a shot down German Heinkel. The first urgent countermeasures to jam this signal was the retuning of hospital SW diathermy machines to 30 MHz and the addition of antennas. These were placed in the open, or on the hospital roofs, and run continuously at night on full power producing radio noise, interfering with the reception of the dots and dashes by the bomber's aircrew. Later, a 30 MHz. transmitter was built which broadcast dashes, in effect bending the German beams. It was code-named "Aspirin" as it cured the headache.